Introducing Stacks — Bringing Programmability to Bitcoin

Introducing Stacks — Bringing Programmability to Bitcoin
What does Stacks blockchain do?
It unlocks programmability. Bitcoin was launched as an asset chain. It’s primary function, at least in the beginning, was to provide a decentralized way of moving and holding a new money. Unlike Ethereum smart contracts, the Bitcoin blockchain itself doesn’t support a wide variety of programmability.
This is what Stacks has set out to solve.
Stacks is the leading Bitcoin Layer-2, enabling smart contracts and decentralized applications to use Bitcoin as a secure base layer. Stacks extends the capabilities of Bitcoin without changing Bitcoin, unlocking billions in latent capital. — https://www.stacks.co/learn/introduction
The Secret 7
Let’s attempt to understand the Stacks blockchain and its relevance for developers by answering the following 7 questions
- Why is it difficult to build on Bitcoin?
- How does Stacks improve the developer experience?
- What is Clarity and how is it different from Solidity?
- What is the architecture of the Stacks chain?
- How does one become a stacker?
- What are the options to earn yield for individual sta(c)kers?
- How can developers participate in this ecosystem?
1. Why is it difficult to build applications on Bitcoin?
1. Limitations of Script Bitcoin uses the Script programming language for programming its smart contracts. For security reasons, this language is purposefully not Turing-complete. It only allows a limited scope when programming smart interactions with the network and prevents looping.
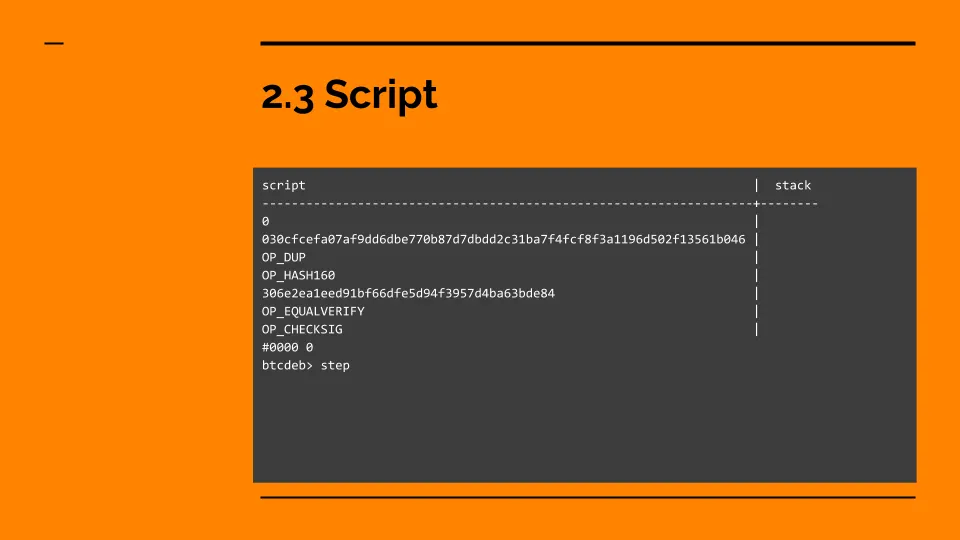
Script is intentionally simplified to prevent security attacks on the network. However, over the years, Bitcoin developers have enhanced the base stack of the code. e.g., developers released the Ordinals Protocol. It allows developers to store data in Bitcoin transactions. As a result, users can now create fungible and non-fungible tokens on Bitcoin.
However, despite these changes actual development on Bitcoin remains throttled by the limitations of Script.
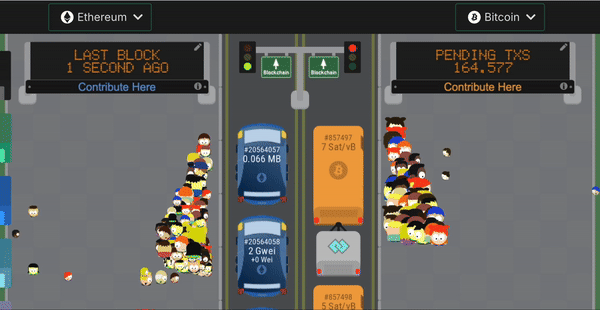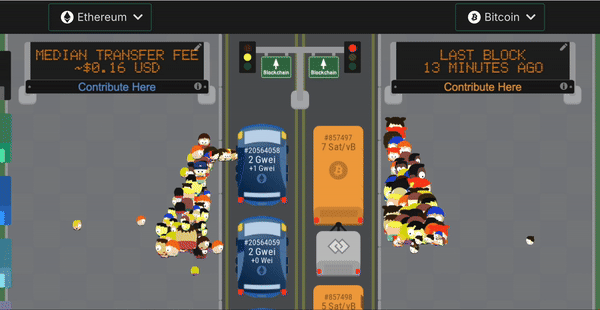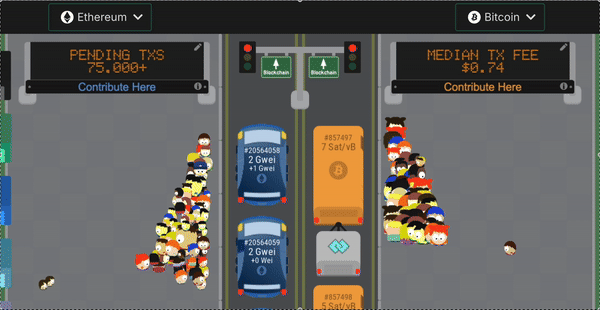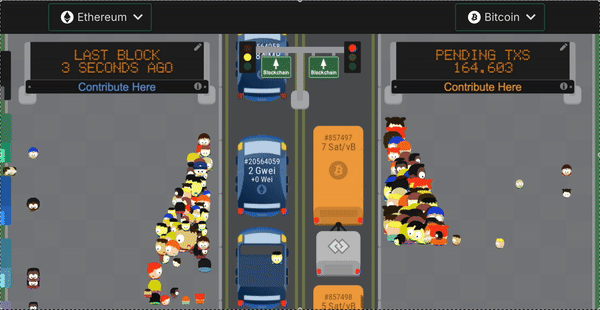
2. Bitcoin’s slow block times
Another problem with building on Bitcoin is that a block gets created only once every 10 minutes. Sometimes even more! It takes 6 blocks to be created after your transaction for it to be finalized. Which means the time to finality in Bitcoin can go beyond 1 hour.
This is untenable for AMMs or lending protocols which need immediate settlement of trade. In comparison Ethereum has a block-time of 15 seconds. Look at the visualization below to see the relative speed.
2. How does Stacks improve the developer experience?
- It uses Clarity, a smart contract language, that enables developers to build a wide range of applications
- It reduces the block-time. Stacks transactions receive finality in the order of seconds so faster applications can be built.
3. What is Clarity and how is it different from what Ethereum uses?
As of August 2024, $85B is locked in DeFi alone. Smart contracts enable the development of apps that collectively form DeFi. On Ethereum, EVM is the virtual machine which enables the execution of smart contracts. The Ethereum smart contracts are written in a language called Solidity. Its counterpart in Stacks is Clarity
Its counterpart in Stacks is Clarity
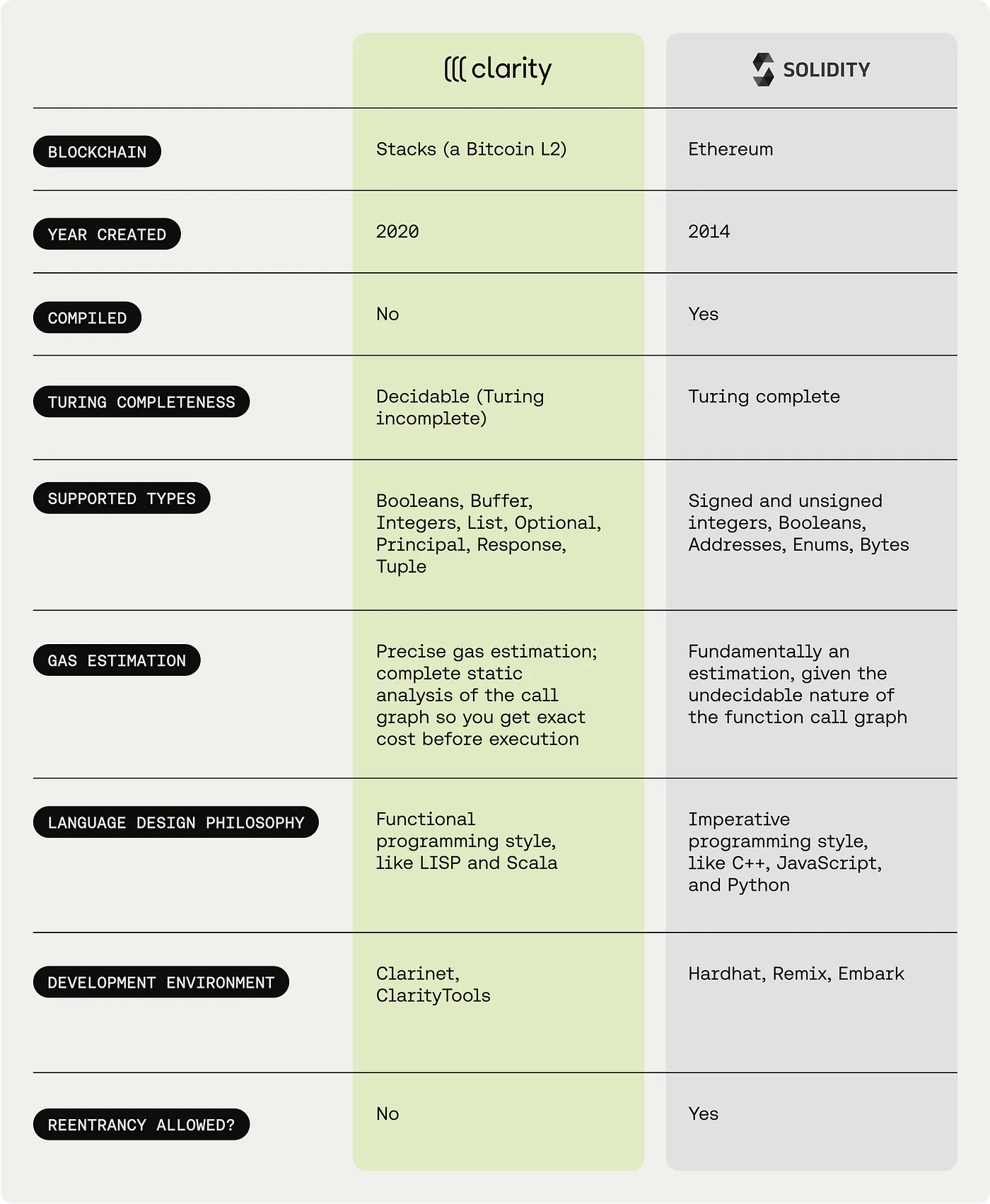
To describe Clarity in detail will take its own article, but for the purposes of this post it is sufficient to know that even though Clarity has a bit of a learning curve, it does bring a host of efficiency and security benefits.
- Decidable language → developers know precisely what an application will (or won’t) do. Making it more secure than Solidity.
- Human readable code → so easier to audit
4. Architecture
Stacks operates on the Proof of transfer consensus mechanism. The following are some of the salient features/design choices.
- PoX
- The Mining Process
- No UTXOs
1. Proof of transfer (PoX) Miners spend bitcoin for the chance to win a stacks tenure. They create multiple blocks within a single bitcoin block. The spent bitcoin goes to the Stackers — users who have locked their STX. Miners propose new blocks and Stackers sign and validate those blocks.
The Stackers receive native BTC, making Stacks as the only protocol that gives native Bitcoin yield as part of its consensus — Andre Serrano
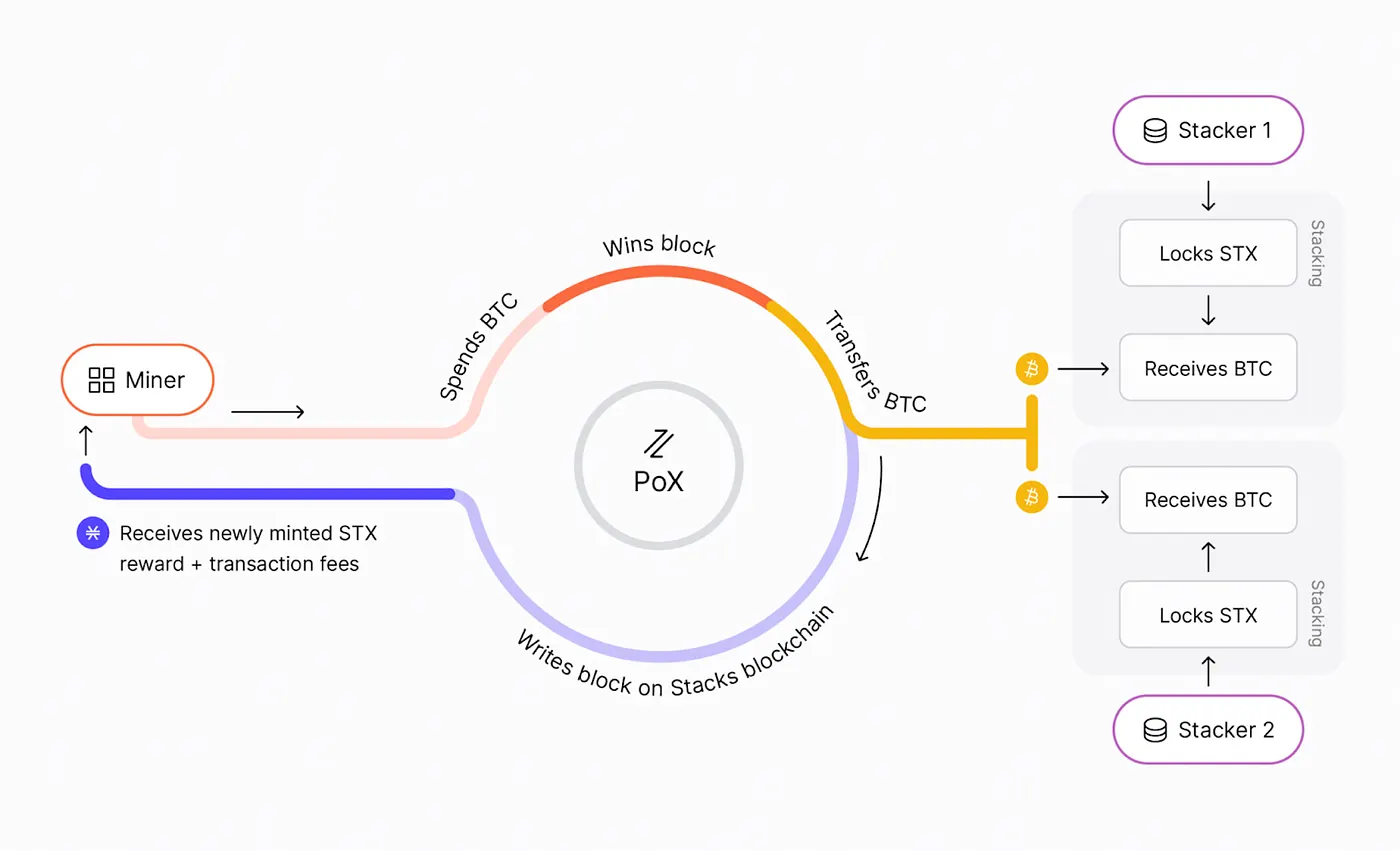
2. Mining Process In the PoX mining process, Stacks miners send a Bitcoin L1 transaction. In this Bitcoin transaction the hash of all of the Stacks block headers is recorded in the OP_RETURNfield. This enables anyone to validate those transactions. On the Bitcoin chain, this is possible because the OP_RETURN field allows storing up to 40 bytes of arbitrary data.
By recording the history of Stacks on the Bitcoin blockchain Stacks inherits Bitcoin’s security. This implies that one has to change the Bitcoin history (to change the OP_RETURNvalues) to alter the history of the Stacks chain.
3. No UTXOs like Bitcoin There are different ways of recording the state of a blockchain. One such way is called the UTXO model. This is what Bitcoin follows.
In contrast, the Stacks network follows the Account Model. In the account model, the global balances of each address are maintained on-chain. On the other hand, in the UTXO model only the change in balance is recorded as transaction receipts. To find the account balance in the UTXO model, one has to some up all the incoming and outgoing change-receipts.
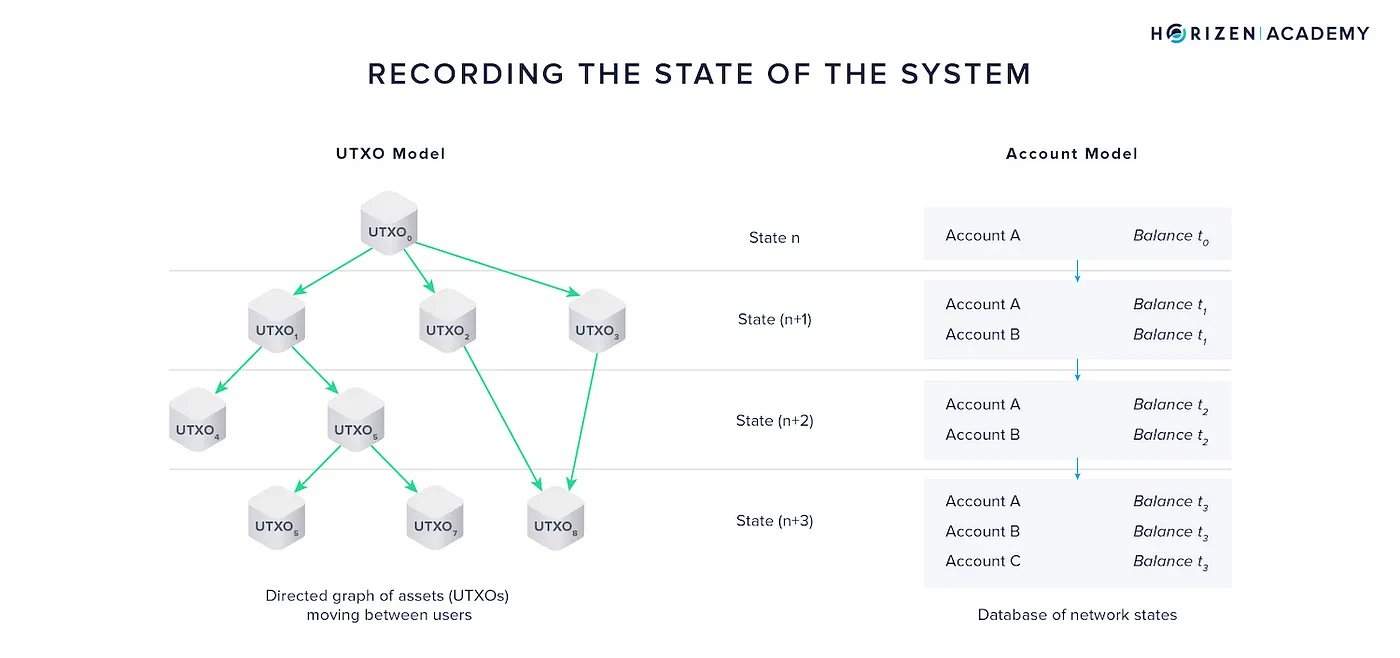
In the UTXO model, the entire graph of transaction outputs, spent and unspent, represents the global state. In the account model, only the current set of accounts and their balances represents the global state. — https://www.horizen.io/academy/utxo-vs-account-model
5. Qualifications to participate in Stacking
- The minimum amount required to participate (validate Stacks blocks) is around a 100K STX per cycle (2 weeks).
- All stackers have to run a Bitcoin D-Node and a stacks node (basically need to keep the Stacks-Signer Binary running to validate the txs)
If the above conditions cannot be met, then a user can participate in various pools set up by established partners like Chorus One.
How do you earn BTC with STX? You can earn BTC with STX through stacking. This process involves temporarily locking STX tokens for about two weeks in exchange for BTC rewards. The Stacks Layer 2 network rewards stackers because they contribute to the security of the protocol.
At today’s prices the 100K minimum requirement amounts to $150K for someone to become a Stacker. This is not a small amount.
How does a solo stacker participate in Stacking?
Through liquid stacking one can start with smaller sums and earn yield. This involves locking your STX tokens on a liquid stacking protocol like StackingDAO to earn bitcoin.

Additionally, stackers also receive a liquid token called Stacked STX (stSTX), which represents the amount of STX locked. Liquid STX stacking became possible recently after April 2023.
Liquid stacking is beneficial because stackers can stack any amount of STX tokens without running a node, as the stacking protocol does it on their behalf.
Participating in Stacks as a developer
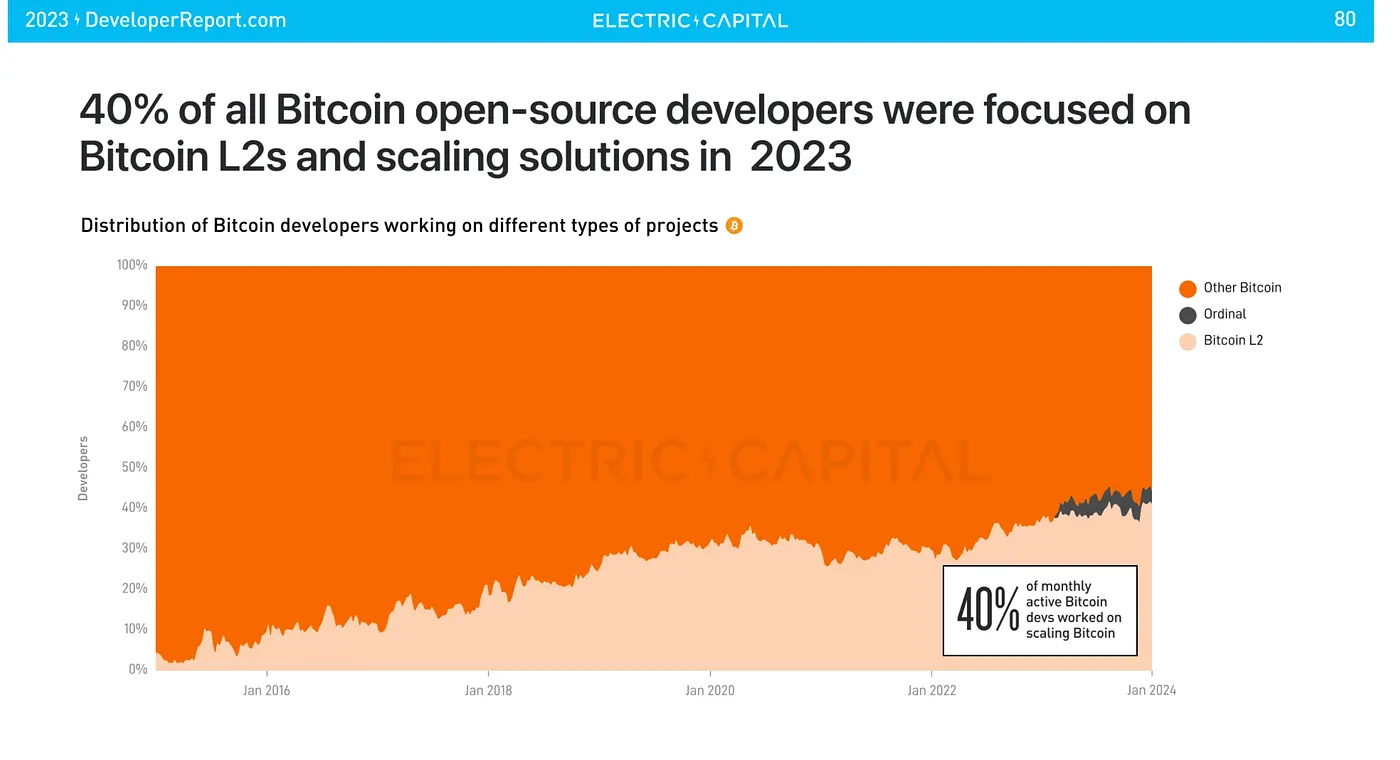
Stacks is a burgeoning ecosystem that holds a lot of potential for Web3 developers
Stacks consistently ranks amongst the top developer ecosystems. sBTC Protocol enables developers to build DeFi applications using smart contracts that can be directly triggered by a Bitcoin transaction. Over the next couple of months core DeFi primitives be launched
- Lending and Borrowing — Allow people to borrow against their Bitcoin e.g. Zest Protocol
- Stablecoin Projects — e.g. Hermetica
- Canonical sBTC and its wrapped forms as a way to connect various other L1 Ecosystems

Bridging
There is a lot of development opportunity that sBTC brings. It is a programmable bitcoin asset backed 1:1 with BTC. Stacks Bitcoin Bridge is an improved bridge with the following unique features
- Miners earn BTC to maintain the bridge (PoX)
- Miners post an STX collateral which bolsters the bridge security
- Miners can’t censor transactions by making sBTC a part of the Stacks consensus. Miners will have to accept the forced inclusion of sBTC transactions.
- Faster deposit and withdrawal times
Stacks is a burgeoning ecosystem that holds a lot of potential for Web3 developers to build a career and impactful applications!
- Browse the Stacks Github for contributing to code and updates
- Get involved with SIPs, which determine how Stacks technology progresses.
- Find jobs of all types from across the ecosystem and get rewarded in STX for recruiting talented people.
- Or join a stacks working group to be involved with the community
Credits
The inspiration for this article was drawn from the Chorus One podcast hosted by Luis Núñez